Politics
Hungary: EU’s Most Corrupt Nation Faces Scrutiny as it Takes the Presidency of the Council
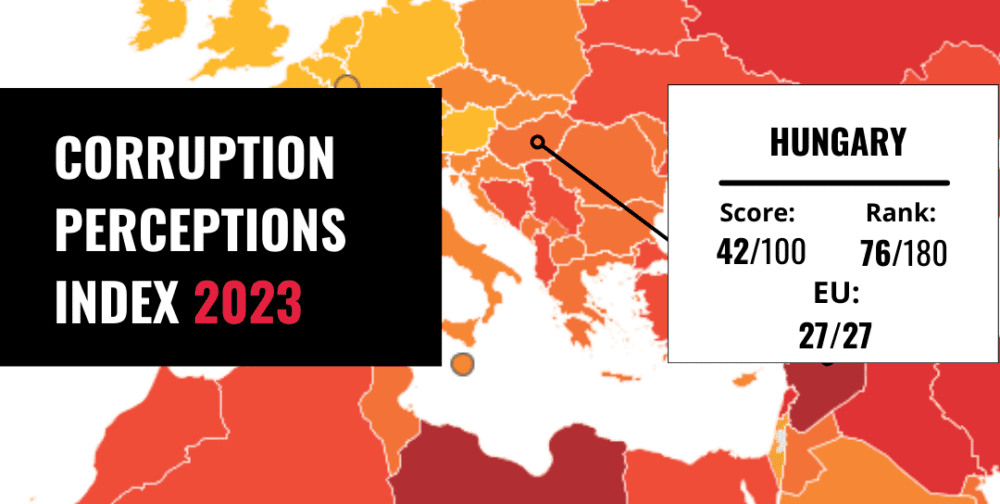
Budapest – Hungary remains the European Union’s most corrupt country, according to the 2023 Corruption Perception Index (CPI) released last January by Transparency International. Despite some judicial reforms aimed at securing EU funds, systemic corruption continues to undermine Hungary’s governance, raising significant concerns as the country became the new chairing member state Presiding the Council of the EU as of July 1, 2024.
Hungary Reigns in the Lowest Rankings
Hungary found itself at the bottom of the list for the year, in a row among EU member states with a score of 42 points on the Corruption Perceptions Index’s 100 point scale, where 0 represents the highest level and 100 the lowest level of perceived corruption. While the country improved slightly in global rankings, rising from 77th to 76th place among 180 countries, this minor advancement does little to counteract the perception and reality of widespread corruption domestically.
The country report, from Transparency International Hungary, released in Budapest, sheds light on the issue of corruption. While some reforms have been implemented, they are deemed insufficient to restore the rule of law and effectively combat corruption.
Judicial Reforms: A Drop in the Ocean
The government of Hungary has made some changes, to its system, due to the influence of the European Union. The EU linked the allocation of cohesion policy funds to these reforms. In December 2023, €10.2 billion were unlocked by the European Commission as a result of these changes representing the disbursement of EU funds after growing worries about Hungary’s lack of adherence to the rule of law.
However Transparency International Hungary has highlighted that these actions fall short in ensuring autonomy. The authority and capabilities of the established Integrity Authority and Anti Corruption Task Force are deemed inadequate in addressing corruption effectively. The governments efforts, such, as enhancing protections for business secrets and imposing obstacles to accessing public interest data are viewed more as steps, than holistic remedies.
Political Motivations Behind the Scrutiny of Transparency International Hungary
The investigation conducted by the Sovereignty Protection Office (SPO) into Transparency International Hungary has further complicated the issues surrounding corruption and governance, in Hungary. Globally Transparency International has criticized this action believing it to be politically motivated to undermine the NGOs corruption activities. This investigation has sparked worries regarding the security of information, within the NGO putting their vital anti corruption work at risk. Hungarian data protection legislation must align with Article 2(1) and Recital (15) of the GDPR to uphold the supremacy of European law and the regulations within the GDPR. According to rulings from the European Court of Justice, Member States are required to adhere strictly to GDPR provisions without deviation.
Economic and Regional Context
Hungary’s economic situation reflects the challenges it faces with corruption. When looking at GDP per person, Hungary falls behind neighboring countries doing better, than Bulgaria, Croatia and Romania within the EU. In comparison, Poland, Czech Republic and Slovakia demonstrate performance and anti corruption efforts.
Although Hungary has a rate of investment, this has not led to economic growth. This suggests that the funds may not have been used effectively due to activities related to public procurement. Transparency International Hungary points out that despite some improvements, in reducing single bid tenders, the public procurement system still struggles with influence and lacks market competition.
Hungary’s Role as Chair of the Council of the EU
As Hungary takes over the presidency of the European Commission, these matters become more important. The leadership position of the country raises concerns, about how various EU priorities, those concerning rule of law and corruption efforts, will be addressed. The examination of Hungary’s actions and their harmony, with EU principles is expected to increase.
Hungary’s standing problems with corruption, along with its prominent position in the EU, underscore the pressing importance of real change and responsibility. While some slight enhancements have been noted in the CPI, they are overshadowed by the ongoing battles against deep-rooted corruption, the non and the absence of judicial autonomy. As Hungary takes on a leading role within the European Commission, global observers will be closely monitoring to see if it can effectively address its corruption issues and pave the way, for transparency and governance.
References:
- Transparency International. (2024). Transparency International Condemns Hungary Investigation.
- AP News. (2024). Hungary Government Investigates Transparency International.
- Transparency International. (2024). Corruption Perception Index.
Politics
Interview with La Tribune Dimanche
Interview with Christine Lagarde, President of the ECB, conducted by Marie-Pierre Gröndahl on 8 May 2025
18 May 2025
The new US President’s first 100 days in office have been a period of economic and financial chaos. What’s the best response to all of this chaos and disruption?
President Trump taking office changed the state of play in three key areas at once: the economy, politics and defence. These have been three key pillars of international cooperation in the increasingly globalised world of recent decades. But this is an opportunity more than a threat – Europe is needed now more than ever. European leaders have to seize this opportunity and speed up the process of deepening the European Union. As we see our reliance on others in the areas of energy, defence and finance being questioned, we need to work together. These are public goods and require coordinated action at the European level. None of the countries in the euro area would be able to tackle the challenges in these three areas on their own.
Can the EU manage to do so?
The EU brings together 450 million people whose purchasing power per capita, standard of living and productivity are lower than in the United States. But the EU also has undeniable strengths and capabilities, starting with the often overlooked fact that our largest trading partner is in fact the EU itself, not the United States. Europe has no option but to rise to this challenge. Just as we are seeing how the rule of law, the courts and trade rules are being challenged in the United States, and how uncertainty is a constant and seems to be renewed every day, Europe is quite rightly seen as a stable economic and political region with a solid currency and an independent central bank. It’s impressive to see that in a period of uncertainty, when the US dollar would usually have strengthened significantly, the opposite has happened and the euro has strengthened compared with the US dollar.
Why?
It is counter-intuitive but can be explained by the level of uncertainty and the fact that some parts of the financial markets are losing confidence in US policies.
How can the EU react to the increase in tariffs announced by Donald Trump?
It needs to have a strong hand should negotiations prove unsuccessful. This means it needs to have identified the relevant sectors, regions, amounts and percentages to be able to determine the retaliatory measures that are available. From a business perspective, it has to negotiate, consider the room for manoeuvre, understand what the other side wants and see whether an agreement can be reached. The fact that the European Commission is seeking common ground with other countries, in Latin America for example, but also India, Indonesia and countries in South-East Asia, is also very relevant.
Can Europe emerge united?
It depends partly on the global challenges we are facing. If all European countries were facing external threats, they would need to take a leap forward together. NATO has so far been working very well in helping to protect Europe. We have now all understood that there was a need to build a common European defence mechanism together. Shared threats can give rise to shared initiatives, as we saw with the Next Generation EU borrowing during the pandemic. “Let’s share our best elements and enrich ourselves with our mutual differences”, as the great European Paul Valéry said.
Many French and European business leaders are disappointed that the recommendations in Mario Draghi’s report have not been acted on. They have also criticised over-regulation in Europe. Do they have a point?
They’re being slightly unfair. It’s true that progress towards greater European integration over the past 50 years has also led to a build-up of regulation. But legislative initiatives like the “Omnibus” packages, which combine multiple amendments or revisions, have kept coming over the past few months. There is political will to reduce reporting obligations and increase efficiency, but this can’t be done overnight. Politicians have a very important role to play here.
The Franco-German relationship is considered to be a driving force of the EU, but it seemed to be losing momentum in recent years. Will the arrival of a new German Chancellor change things?
The meeting between Emmanuel Macron and Friedrich Merz on 7 May sends a very strong signal. As does the announcement by the new Chancellor of a €500 billion infrastructure investment programme, in addition to a significant increase in defence spending. This is a major change for Germany. This Franco-German partnership, without which few initiatives would get off the ground, seems committed to acting together. Certain projects, like the capital markets union, had been on hold for a few years because the Franco-German partnership wasn’t working so well. These two leaders understood that it would be necessary to mobilise funds at the European level and build platforms to attract those who want to invest in it. And there are many who want to.
What needs to be done to stop a large proportion of European savings from being invested in the United States?
We need to create European solutions that help us avoid the type of dependence we had for energy, particularly for payment infrastructures and the digital euro. The major payment providers, which account for just over 60% of the market, are not European. Digital payment systems do exist in some EU countries, but none have pan-European reach. The European Parliament needs to act on the draft legislation that has been under discussion since July. I think there is the political momentum for things to move a bit faster. The digital euro is a topic that the ECB is working on jointly with the Parliament, which has to approve the project. On our side, as of October we will be technically ready to complete the preparations to implement and gradually scale up the project.
Can Europe catch up in these two areas?
Definitely. We need to develop a smart regulatory framework. Europe is not the Wild West. For the digital euro and the capital markets union, the groundswell is the strongest I’ve seen in the six years I have been at the ECB. We also need to harmonise supervision, like we have successfully done for banking.
Does this period worry you?
I’m not at all pessimistic. In Europe, employment is holding up, purchasing power is increasing and inflation is falling. Consumption and investment should pick up again, even if the uncertainty sparked by the US Administration’s announcements is weighing on confidence and holding back that recovery. However, I think we need to demonstrate a shared desire to free ourselves from the energy, military and financial dependencies we naively lulled ourselves into. It’s a rude awakening, but we can rise to the challenge – Europe has already partially shown that by diversifying its energy supply sources. And we should further reduce gas supplies that come from Russia. I am intentionally being positive, because I also think that’s the approach we have to take. Europeans tend to be less optimistic than Americans – I’ve spent enough time living in the United States to be able to say that with at least a small amount of credibility. We tend to approach things more critically. But being positive certainly does not mean ignoring the reality of the situation.
Precisely, the falsehoods are piling up, including where economics is concerned. How does one fight against this phenomenon?
It’s another challenge we’re being confronted with – what is and isn’t true. We should all check facts and figures, and the authenticity of everything that is reported. Journalists have a fundamental duty in this regard.
Is globalisation being called into question?
I think globalisation has had an underlying legitimacy issue for a long time. Even though it has been very beneficial for some countries and has saved hundreds of millions of people from famine, it has also followed, perhaps too closely, a logic of cost reduction, efficiency and fragmentation. And that’s without considering the issues of deindustrialisation and the impoverishment of certain regions or geographical areas that have been tragically affected by it. These issues have of course been exploited for electoral gain. But they should nevertheless give us cause to rethink how our economic relations, our supply sources and our payment infrastructures are organised, also with the aim of preserving the European social model, which is more protective than others.
The IMF has recently published some fairly negative forecasts for France in terms of debt reduction and the deficit. What is your opinion?
Every country, no matter its debt level or its deficit-to-GDP ratio, can decide to set its public finances on a new trajectory. In European fora, such as ECOFIN [the Economic and Financial Affairs configuration of the Council of the EU] or the Eurogroup, the French authorities have expressed their determination to reduce the budget deficit and the debt level. These intentions must become reality. It’s a question of credibility – a question that every country is facing.
The US President has attacked both the strategy of the Federal Reserve and its Chair, Jay Powell, on several occasions. Would such a thing be conceivable in Europe?
The independence of the European Central Bank is guaranteed by the Treaties. So no, that would not be possible. Central bank independence is fundamental if a country, or group of countries, is to have a healthy monetary and financial system. It has never ended well when a central bank has found itself under the thumb of a fiscal authority.
Politics
In a New Chapter in EU Enlargement Antonio Costa Reinforces Commitment to Western Balkans Amid Albanian Momentum
TIRANA — In a clear signal of the European Union’s renewed resolve on enlargement, European Council President António Costa concluded a strategic tour of the Western Balkans with a high-profile visit to Albania on May 15, 2025. Speaking at a joint press conference with Prime Minister Edi Rama following recent parliamentary elections that saw Rama secure yet another decisive victory, Costa declared that “Albania is on track to join the European Union” and affirmed that the EU’s expansion into the region represents “the most important geopolitical investment we are doing.”
The timing of Costa’s remarks is significant. After years of stalled progress and skepticism surrounding the credibility of EU enlargement, particularly during the turmoil of Brexit and the migration crisis, the bloc appears to be recalibrating its focus toward the Western Balkans — not only as a moral imperative but as a strategic necessity.
A Geopolitical Imperative
Costa’s statement that the enlargement process is the EU’s “most important geopolitical investment” marks a shift from previous cautious tones, especially compared to the lukewarm approach taken by some member states in recent years. The context for this urgency is multifaceted: Russia’s ongoing war in Ukraine has reinvigorated Eastern Europe’s desire for closer EU integration, while China’s growing influence in Southeastern Europe through infrastructure investments and trade agreements has raised concerns within Brussels.
In this light, Albania — along with Serbia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Kosovo — represents both a frontier of democracy and a buffer against external interference. By anchoring these nations more firmly within the EU’s orbit, the bloc aims to stabilize a historically volatile region and ensure long-term security and prosperity.
Albania’s Moment?
Prime Minister Edi Rama’s landslide electoral victory this week was hailed by Costa as further evidence of Albania’s popular commitment to EU integration. “The result of the elections this week re-confirms the desire of Albanians for European Union integration,” Costa said, extending his congratulations to Rama.
This sentiment resonates with many Albanian citizens who have long viewed EU membership as a pathway to economic development, institutional reform, and regional stability. However, some critics argue that Rama’s continued dominance — now entering its fourth term — raises concerns about democratic backsliding, including issues related to media freedom and political polarization.
Still, Costa emphasized that the accession process is no longer a matter of “if” or “how,” but rather “when.” This framing reflects a broader consensus emerging within the EU leadership that the time is ripe for accelerated negotiations — provided key reforms are implemented.
Reform Remains the Linchpin
Despite the optimism, Costa did not shy away from issuing a challenge to Albania’s government: “You know exactly what needs to be done; I can only encourage you to keep your eyes on the objective and deliver on these last milestones.”
Chief among those priorities remain the rule of law, judicial independence, and the fight against corruption — areas where Albania has made progress but still faces criticism from watchdog groups and the European Commission alike. The country opened formal accession negotiations in March 2024, becoming the first Western Balkan nation to do so under the revised enlargement methodology introduced in 2020.
To bolster cooperation, the EU and Albania launched their first-ever Security and Defence Dialogue earlier this year, underscoring a shared interest in addressing hybrid threats, cyber insecurity, and regional defense coordination. As Costa noted, “We stand together on the global stage,” signaling that Albania’s future role in European security architecture will be central to its integration process.
Tirana Steps onto the European Stage
Another highlight of Costa’s visit was the upcoming European Political Community (EPC) summit, set to take place in Tirana on May 16 — the first such meeting ever hosted in the Western Balkans. Welcoming over 40 European leaders, the EPC gathering will provide Albania with an unprecedented platform to showcase its readiness for deeper European integration.
Costa praised the organization of the event, calling it “impressive,” and used the occasion to commend former EU High Representative Federica Mogherini for spearheading the establishment of a new campus of the College of Europe in Tirana. Named after EU icon Jacques Delors, the inaugural class — the “Jacques Delors Promotion” — symbolizes more than academic collaboration; it represents the EU’s investment in cultivating a new generation of European-minded leaders in the region.
“Europe is not only about prosperity, it is not only about values. Europe needs faith for the future, for our common future together,” Costa reflected, emphasizing the emotional and ideological dimensions of enlargement.
Looking Ahead: A Legacy in the Making
Costa’s reference to 1992 — when the Maastricht Treaty formally established the European Union — was a deliberate nod to the transformative potential of the moment. Just as the early 1990s marked a turning point for European unity post-Cold War, the current juncture may well define the next era of European integration.
With Albania poised to become the first Western Balkan country to join the EU in the coming decade, the path forward remains challenging but increasingly plausible. If successful, it could catalyze momentum across the region, offering hope to millions in neighboring countries still waiting for their own invitations to join the European family.
As Costa put it, echoing both history and aspiration: “It is the moment, like it was in ’92, to make another big step.” And in this race toward Europe, Albania, for now, seems to be leading the pack.
During his visit to the Western Balkans, European Council President António Costa met with Albanian Prime Minister Edi Rama in Tirana. At the joint press conference, he reaffirmed the EU’s strong commitment to Albania’s accession, praised the country’s reform progress, and commended its role in hosting the upcoming European Political Community summit. He also welcomed the opening of a College of Europe campus in Tirana, highlighting Albania’s deepening ties with the EU.
Source link
Politics
EU Unveils Major Agricultural Reform to Boost Competitiveness and Ease Burden on Farmers
In a significant move aimed at revitalizing the European agricultural sector, the European Commission has unveiled a comprehensive package of reforms designed to simplify the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and enhance the competitiveness of farmers across the bloc. Announced on May 14, 2025, the new measures target administrative inefficiencies, streamline regulatory requirements, and improve crisis response mechanisms — all while delivering substantial cost savings and greater flexibility for both farmers and national administrations.
A Bold Step Toward Simplification
The reform package is part of the European Union’s broader effort to reduce red tape and support economic resilience, as outlined in the Competitiveness Compass . By simplifying rules and procedures, the Commission aims to make agriculture more attractive, especially to small-scale and young farmers, while also promoting sustainability and digital innovation.
According to the Commission, these changes could save up to €1.58 billion annually for farmers and €210 million for national authorities , freeing up resources that can be reinvested into farm development, environmental protection, and rural economies.
Key Highlights of the Reform Package
Simplified Payment Scheme for Small Farmers
One of the most notable changes is the doubling of the annual lump-sum payment limit for small farmers from €1,250 to €2,500 . This measure is intended to:
- Promote a fairer distribution of CAP support,
- Encourage economic vitality in rural areas,
- Reduce bureaucratic obligations for small farms and public authorities alike.
Small farmers benefiting from this scheme will also be exempt from certain environmental conditionality rules, although they may still receive eco-scheme payments for adopting environmentally friendly practices.
Easier Environmental Compliance
To reflect the diversity of farming practices and regional conditions, the Commission is introducing more flexible environmental requirements:
- Certified organic farms will automatically meet some EU environmental standards.
- Farmers involved in protecting peatlands and wetlands under GAEC 2 will receive incentives and support to comply with stricter national regulations.
This approach ensures that farmers are rewarded fairly for their environmental stewardship without being overwhelmed by overlapping or redundant rules.
Modernized Controls Using Technology
The use of satellite data and other digital tools will significantly reduce the need for on-site inspections. Under the new framework:
- Each farm will undergo only one on-the-spot check per year , minimizing disruption and saving time for both farmers and inspectors.
This shift reflects the EU’s commitment to leveraging technology to improve efficiency and transparency in agricultural monitoring.
Enhanced Crisis Response Tools
Farmers facing natural disasters, animal diseases, or market shocks will benefit from more accessible and flexible crisis management instruments:
- New crisis payments will be available through CAP Strategic Plans.
- Member States will have greater autonomy to adjust their plans, provided they obtain prior approval from the Commission for strategic amendments.
These changes aim to ensure faster, more targeted support during emergencies, strengthening the resilience of Europe’s agricultural sector.
Digitalization and Interoperability
The Commission is pushing forward with its “report once, use multiple times ” principle, encouraging national administrations to develop integrated digital systems. This means:
- Farmers will submit data only once through a centralized system.
- The same data will be used across different reporting requirements, reducing duplication and improving efficiency.
Additionally, small farmers will gain easier access to funding through a new lump-sum grant of up to €50,000 to help modernize their operations and improve competitiveness.
Looking Ahead: A Broader Agenda for Regulatory Reform
This CAP simplification package builds on earlier reforms introduced in 2024 and aligns with the Commission’s Vision for Agriculture and Food , launched in February 2025. It is also part of a wider cross-sectoral initiative aimed at cutting unnecessary bureaucracy across the EU economy.
The legislative proposal will now be submitted to the European Parliament and Council for adoption. Later this year, the Commission plans to introduce further simplification measures targeting non-agricultural policies that impact farmers and agri-food businesses.
As part of its current mandate, the Commission has committed to achieving a 25% reduction in overall administrative burdens and 35% for SMEs , ensuring that EU rules remain effective but not overly burdensome.
Conclusion: Farming for the Future
With today’s announcement, the European Commission has taken a decisive step toward creating a more agile, farmer-friendly, and sustainable agricultural policy. By easing compliance, supporting innovation, and empowering small producers, the EU is laying the groundwork for a stronger, more resilient farming sector capable of meeting future challenges — from climate change to global market volatility.
For Europe’s farmers, the message is clear: the road ahead will be less bureaucratic, more supportive, and increasingly aligned with the realities of modern agriculture.
Source link
-
EU & the World4 days ago
Who Is Valeria Marquez? About the Influencer Who Was Shot During Livestream
-
EU & the World5 days ago
Cardi B & Offset’s Relationship Timeline: From Marriage To Cheating Drama & Split
-
EU & the World2 days ago
Chris Brown Tour 2025: Updates on Concert Dates, Cities, Ticket Prices & More
-
Politics6 days ago
EU Assesses Support for Ukrainian Refugees: Challenges and Flexibility in Humanitarian Response
-
EU & the World3 days ago
Who Is Ben Cohen? About the Ben & Jerry’s Co-Founder Who Was Arrested During Senate Hearing
-
Sports7 days ago
Matteo Berrettini forced to retire amid tears at Internazionali d'Italia
-
Travel5 days ago
Crete earthquake: Is it safe to travel to the Greek island following tsunami warning?
-
EU & the World6 days ago
Justin Dior Combs: 5 Things to Know About Diddy’s Son