Politics
Media Freedom Act: a new bill to protect EU journalists and press freedom | News
Under the new law, adopted by 464 votes in favour to 92 against and 65 abstentions, member states will be obliged to protect media independence and all forms of interventions in editorial decisions will be banned.
Protecting journalists’ work
Authorities will be prohibited from pressing journalists and editors to disclose their sources, including by detaining them, sanctions, office searches, or by installing intrusive surveillance software on their electronic devices.
Parliament added sizeable safeguards to allow the use of spyware, which will be possible only on a case-by-case basis and subject to authorisation by a judicial authority investigating serious crimes punishable by a custodial sentence. Even in these cases, subjects will have the right to be informed after the surveillance has occurred and will be able to challenge it in court.
Editorial independence of public media
To prevent public media outlets from being used for political purposes, their heads and board members should be selected through transparent and non-discriminatory procedures for sufficiently long terms of office. It will not be possible to dismiss them before their contract ends, unless they no longer meet the professional criteria.
Public media will have to be financed using transparent and objective procedures, and the funding should be sustainable and predictable.
Transparency of ownership
To enable the public to know who controls the media and what interests may influence reporting, all news and current affairs outlets regardless of their size will have to publish information about their owners in a national database, including if they are directly or indirectly owned by the state.
Fair allocation of state advertising
Media will also have to report on funds received from state advertising and on state financial support, including from non-EU countries.
Public funds to media or online platforms will have to be allocated via public, proportionate and non-discriminatory criteria. Information on state advertising expenditure will be public, including the total annual amount and the amount per outlet.
Protecting EU media freedom from big platforms
MEPs made sure to include a mechanism to prevent very big online platforms, such as Facebook, X (formerly Twitter) or Instagram, from arbitrarily restricting or deleting independent media content. Platforms will first have to distinguish independent media from non-independent sources. Media would be notified when the platform intends to delete or restrict their content and have 24 hours to respond. Only after the reply (or in the absence of it) may the platform delete or restrict the content if it still does not comply with its conditions.
Media will have the option to bring the case to an out-of-court dispute settlement body and request an opinion from the European Board for Media Services (a new EU board of national regulators to be set up by the EMFA).
Quotes
“The significance of media plurality for a functioning democracy cannot be stressed enough”, rapporteur from the Culture and Education Committee Sabine Verheyen (EPP, DE) said in the plenary debate. “Press freedom is threatened worldwide, including in Europe: the murder in Malta, threats to press freedom in Hungary and many other examples clearly prove that. The European Media Freedom Act is our answer to this threat and a milestone in European legislation. It values and protects the double role of media as businesses and as guardians of democracy”, she concluded.
The rapporteur from the Civil Liberties Committee Ramona Strugariu (Renew, RO) said: “Journalists now have an ally, a set of tools that protects them, boosts their independence and helps them face challenges, interference and the pressure that they are often confronted with in their job. This Regulation is a response to Orbán, Fico, Janša, Putin and those who want to transform media into their own propaganda tools or spread fake news and destabilise our democracies. No journalist should ever fear pressure of any sort when doing their job and informing citizens.”
Background
In adopting this report, Parliament is responding to citizens’ expectations for the EU as expressed in the conclusions of the Conference on the Future of Europe:
– to introduce legislation addressing threats to media independence and enforce EU competition rules in the media sector, in order to prevent large media monopolies, as well as to ensure media pluralism and independence from undue political, corporate and/or foreign interference (Proposals 27(1), (2));
– counter disinformation through legislation and guidelines for online platforms and social media companies (33(5));
– defend and support free, pluralistic and independent media and ensure the protection of journalists (37(4)).
Politics
European Parliament begins its 10th term
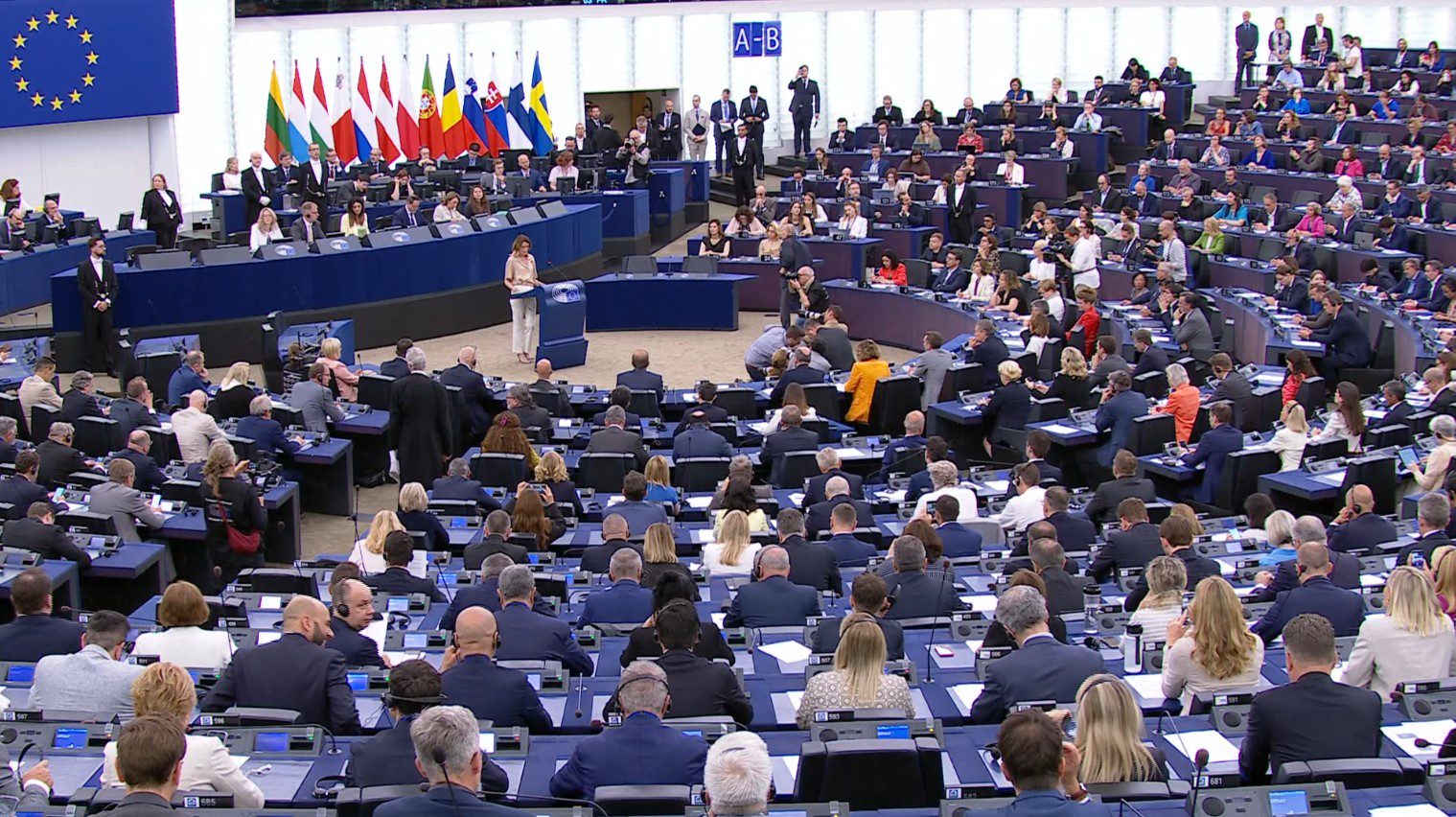
European Parliament Convenes in Strasbourg: New President to be Elected amid Growing Diversity
On a momentous Tuesday in Strasbourg, the European Parliament, following the recent European elections held on 6-9 June, officially commenced its proceedings. The session, presided over by the outgoing EP President, Roberta Metsola of the EPP from Malta, commenced with a musical interlude before Pina Picierno, the second Vice-President in the outgoing Parliament from Italy’s S&D, announced the contenders for the coveted Presidency of the Parliament.
The highly anticipated vote, conducted through a secret paper ballot, is set to occur immediately after the inaugural session. To ensure a fair process, eight MEPs, selected by lot, will oversee the election proceedings.
The distinguished candidates vying for the Presidency are Roberta Metsola representing EPP from Malta and Irene Montero from The Left in Spain. Ahead of the crucial vote, both candidates delivered succinct statements to the plenary, outlining their visions for the future of the European Parliament.
To attain victory, a candidate must secure an absolute majority of valid votes cast, which equates to 50% plus one. In the event of no clear winner in the initial round of voting, subsequent rounds may follow with the possibility of new or existing candidates being nominated under the same stipulations. If needed, a third round could ensue with the same regulations. Should no candidate emerge victorious after the third round, the two candidates with the highest votes in this round will advance to a decisive fourth and final round, with the majority winner emerging triumphant.
Upon the election of the new President, the distinguished individual will assume the leadership position and deliver a notable opening address, setting the tone for the parliamentary term ahead.
In this landmark tenth term, the European Parliament boasts 720 seats, an increase of 15 from the previous legislature. Notably, 54% of MEPs are fresh faces, marking a slight decrease from the 2019 intake of 61%, with the representation of women comprising 39%, down marginally from the 40% mark in 2019.
Among the diverse MEP cohort, Lena Schilling, a 23-year-old from Austria representing Greens/EFA, stands as the youngest member, while the seasoned Leoluca Orlando from Italy, a Green/EFA representative aged 77, holds the distinction of the oldest MEP. The average age of MEPs stands at 50, reflecting a diverse range of experiences and perspectives within the parliamentary body.
As the tenth term commences, the European Parliament encompasses eight political groups, an increase from the previous session. Additionally, 32 MEPs remain non-attached, underscoring the dynamic landscape of political affiliations within the Parliament and highlighting the vibrant tapestry of representation in the European legislative body.
Politics
For the first time in 40 years, the Olympics will not be broadcast in Russia

Not a single TV channel, streaming platform or cinema in Russia will show the competitions from the Summer Olympics in Paris, which begin on July 26, sports.ru writes. This happened for the first time in 40 years, when in 1984 the USSR boycotted the Olympics in Los Angeles.
The official explanation is that this time only 16 athletes will participate under a neutral flag, without an anthem and in “unpopular sports”. The unofficial thing is that this is a purely political decision of the Kremlin, and heads of federations call those who agreed to participate traitors, homeless people and foreign agents.
Paris Mayor on Russians at the 2024 Olympics: It would be better if they didn’t come
Anne Hidalgo condemned the International Olympic Committee’s decision regarding representatives of the aggressor country, she said already in March.
According to the official, it would be good if athletes from the terrorist country did not participate in international competitions.
“I prefer that they not come. We cannot act as if the invasion does not exist. We cannot act as if Putin is not a dictator who is threatening all of Europe today.”
At the same time, she added that such sanctions cannot be imposed against Israeli athletes, since Israel’s actions are different from Russia’s aggression.
“There can be no talk of imposing sanctions against Israel in connection with the Olympic and Paralympic Games. Because Israel is a democratic country,” the mayor told Reuters.
Photo: Social Network / korrespondent.net.
Politics
Keir Starmer Secures Historic Labour Victory, Ending 14 Years of Conservative Rule in UK
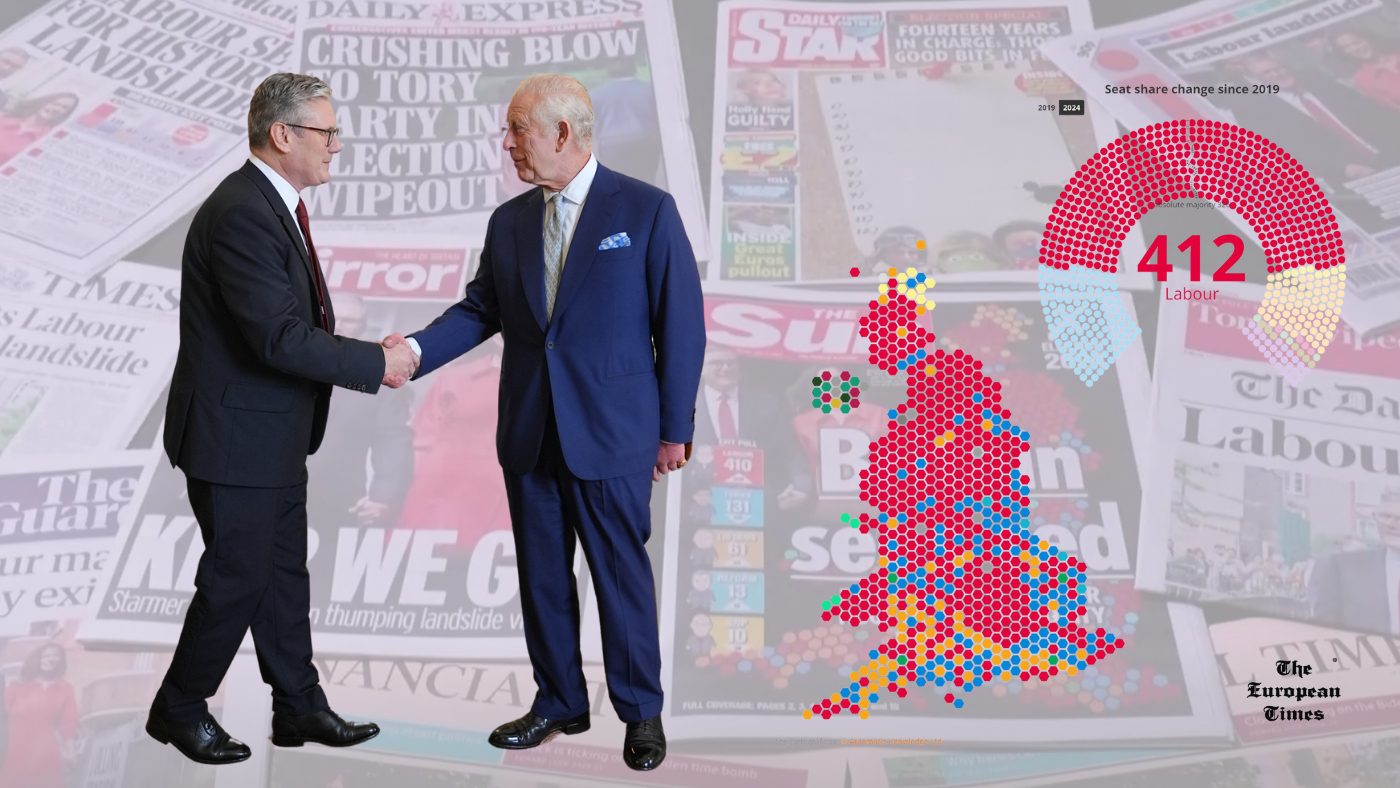

London – In a seismic shift in British politics, the Labour Party, led by Keir Starmer, has achieved a resounding victory in the UK general election, bringing an end to 14 years of Conservative governance. The results, which had been foreshadowed by months of polling, have given Labour its strongest parliamentary majority since 2001.
Labour secured an impressive 412 seats, far surpassing the 326 required for an absolute majority and more than doubling their 2019 performance. This landslide victory marks a dramatic turnaround for the party and signals a clear desire for change among the British electorate.
Upon learning of his victory in his central London constituency, Starmer declared, “The people have spoken, and they are ready for change.” This statement encapsulates the mood of a nation seemingly eager to embark on a new political chapter.

The Conservative Party, in stark contrast, suffered its worst defeat since its founding in 1834. The Tories lost at least 250 seats compared to their 2019 performance under Boris Johnson, ending up with a mere 121 seats. This historic collapse prompted the outgoing Prime Minister, Rishi Sunak, to apologize to “those Conservatives who have lost despite their dedication” while congratulating Starmer on his victory.
The election also saw significant shifts for other parties. The Liberal Democrats, led by Ed Davey, emerged as the third-largest party with 71 seats, a gain of 63 from the previous election. The Scottish National Party (SNP) experienced a dramatic decline, securing only nine seats, a loss of 38 compared to 2019. Sinn Fein, the Irish republican party, maintained its seven seats.

In a surprising development, the nationalist-populist Reform UK, led by Nigel Farage, entered Parliament with four seats, exceeding all poll predictions. The Green Party quadrupled its representation, winning four seats in total.
Starmer’s first address as Prime Minister was filled with promises of change and renewal. “We did it!” he exclaimed, emphasizing that Britons would wake up to find “a weight has finally been lifted from the shoulders of this great nation.” He stressed the urgency of rebuilding trust in politics and committed to serving all citizens, regardless of their voting preferences.
The new Prime Minister outlined his government’s priorities, including improving security on streets and borders, rebuilding infrastructure, and enhancing opportunities in education and employment. “Changing a country isn’t as easy as pressing a button,” Starmer cautioned, “We will rebuild the United Kingdom, brick by brick.”
Rishi Sunak, in his farewell speech, acknowledged the clear signal for change sent by the electorate. “I have heard your anger and disappointment. I take responsibility for these results,” he stated. Sunak announced his intention to step down as Conservative Party leader, but not immediately, allowing time for a formal process to choose his successor.
The election also marked a personal triumph for Nigel Farage, who finally won a parliamentary seat on his eighth attempt, representing Clacton-on-Sea. Farage hailed his party’s performance as “extraordinary” and vowed to fill what he sees as a “huge void in the center-right.”
In regional developments, Sinn Fein became the largest Northern Irish party in the British Parliament for the first time, maintaining its seven seats while the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) fell to four. In Scotland, the SNP lost its dominance, dropping from 48 seats in 2019 to just 8, with Labour making significant gains. Wales saw the Conservatives lose all representation, with Labour dominating the results.
As the United Kingdom enters this new political era under Starmer’s leadership, the country faces significant challenges. The incoming government must address economic concerns, social policies, and perhaps most critically, work to restore public trust in the political system. The scale of Labour’s victory suggests a strong mandate for change, but the real test lies in translating this electoral success into effective governance in the years to come.
-

 Sports7 days ago
Sports7 days agoOfficial: Juventus announces sixth purchase
-

 Health & Society7 days ago
Health & Society7 days agoThe intoxicated society
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoThe Russian patriarch to Putin: You are the first truly Orthodox president
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoBeautiful Juve: Vlahovic and youth rout Verona. Thiago Motta first
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoJuventus, Vlahovic: “Now we play a different game.”
-

 Politics4 days ago
Politics4 days agoEU Intensifies Pressure: Six-Month Extension of Russia Sanctions
-

 Health & Society3 days ago
Health & Society3 days ago7 Superfoods That Will Boost Your Fitness Results
-

 EU & the World5 days ago
EU & the World5 days agoBrittany Cartwright Files for Divorce From Jax Taylor After 5 Years of Marriage








