Health & Society
Proactive Steps To Ensure Health Security In European Politics

Most people underestimate the integral role health security plays in European politics. In a landscape fraught with health crises and political instability, it is imperative that you take proactive steps to enhance this security. By understanding the interconnectedness of health policies, governmental actions, and public trust, you can contribute to a more resilient future. Adopting measures such as promoting international cooperation, strengthening healthcare systems, and prioritising mental health will not only safeguard your community but also foster stability across Europe.
Understanding Health Security
Before addressing the intricacies of health security in European politics, it is crucial to grasp what health security entails. Health security primarily involves the protection of populations from health threats, including infectious diseases, environmental hazards, and bioterrorism. It not only concerns individual health but also the broader social and economic stability that can be undermined by health crises. The importance of health security becomes evident when you consider how interconnected our societies are; a health threat in one region can quickly escalate to affect others, underscoring the need for collaborative strategies to mitigate potential risks.
Definition and Importance
The term ‘health security’ signifies far more than just the absence of disease. It encompasses the systems, policies, and practices designed to prevent and respond to health threats. As you consider your part in this, you must acknowledge that robust health security contributes to societal resilience, enabling communities to withstand and recover from health shocks. The economic repercussions of health crises — whether through lost productivity, increased healthcare costs, or destabilisation of markets — highlight the pressing need for proactive measures to safeguard public health.
Current Landscape in Europe
On examining the current landscape of health security in Europe, it is evident that various challenges persist, particularly in light of recent global health emergencies. The COVID-19 pandemic illuminated significant gaps in preparedness and response mechanisms, revealing that Europe’s health systems often struggled to manage crises effectively. Moreover, the rise of antimicrobial resistance and climate change further complicates the health security framework, necessitating a comprehensive approach that encompasses not only immediate health responses but also long-term strategies to enhance resilience.
Consequently, European nations are re-evaluating their health security strategies, aiming to strengthen collaboration across borders and improve response frameworks. By investing in research, fostering communication among member states, and enhancing surveillance measures, you will find that the continent is gradually shifting towards a more integrated health security approach. It’s crucial to remain vigilant, as the volatility of health threats continues to escalate, making it imperative that you advocate for proactive policies that prioritise health security, thereby safeguarding your community and the wider society.
Political Frameworks for Health Security
If you are keen to understand how health security is effectively managed within European politics, you will find that it hinges upon robust political frameworks. These frameworks are largely shaped by the collaborative efforts of various institutions and national policies that seek to mitigate risk and enhance public health outcomes across the continent. As health crises can transcend borders, the response requires a coordinated political structure that not only addresses immediate threats but also prepares for future challenges by prioritising prevention, preparedness, and response strategies.
Role of European Union Institutions
At the heart of European health security lies the role of the European Union (EU) institutions, which are pivotal in formulating policies and programmes. The European Commission, for example, actively develops legislation aimed at harmonising health standards and ensuring that member states collaborate efficiently during public health emergencies. Additionally, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) plays a vital role in monitoring and reporting health threats, providing data-driven insights that help in shaping evidence-based decisions across the region.
National Policies and Collaborations
For you to fully appreciate the dynamics of health security in Europe, it is important to consider how individual nations contribute through their own policies and collaborate with each other. Each member state is responsible for implementing national health policies that align with EU regulations while addressing specific local health challenges. This dual approach allows for tailored responses that are both relevant and effective, fostering partnerships that enhance the overall response to health emergencies.
Considering the diverse healthcare systems and political environments across Europe, your awareness of how national policies are developed is imperative. These policies often embrace a multi-sectoral approach that involves not only health authorities but also various stakeholders, such as educational institutions and non-profit organisations. By leveraging local expertise and resources, nations can build agile collaborations that respond quickly to health threats and maintain a collective resilience against future risks. This synergy is paramount in fostering an interconnected health security landscape that can stand up to challenges that are intrinsic to the European Union as a whole.
Proactive Strategies for Risk Mitigation
Now, embracing proactive strategies for risk mitigation in health security is crucial in the evolving landscape of European politics. These strategies encompass a variety of approaches that aim to prevent, identify, and manage health risks effectively. By prioritising these methods, you can fortify your community against potential threats, ensuring a more resilient public health framework.
Surveillance and Early Detection
Surveillance systems play a vital role in monitoring public health trends and facilitating early detection of potential outbreaks or health crises. By investing in comprehensive surveillance programs, you enable health authorities to promptly identify emerging threats, ensuring that timely interventions can be implemented. This includes utilising technology and data analytics to track disease patterns and pinpoint unusual occurrences that could signify a developing health issue.
Public Health Infrastructure Enhancement
After establishing effective surveillance mechanisms, the next step is to enhance public health infrastructure. This involves strengthening healthcare systems, improving facilities, and expanding access to services. By investing in robust infrastructure, you ensure that health services not only respond swiftly to crises but also maintain a higher standard of care during normal operations. Your community will benefit from well-equipped hospitals, trained healthcare professionals, and efficient logistics systems that can adapt to various health challenges.
Considering the importance of public health infrastructure enhancement, you must focus on collaboration between government entities and healthcare providers. This collaboration can foster innovations in health delivery and expand training programs for healthcare workers, ensuring they are equipped to handle emergencies and everyday healthcare needs alike. By establishing a network of shared resources and seamless communication, you can significantly optimise health outcomes across Europe, paving the way for a healthier future for all citizens.
Cross-Border Cooperation
Once again, you are invited to consider the significance of cross-border cooperation in enhancing health security within European politics. This collaboration ensures that nations can jointly navigate the challenges posed by health crises, which frequently do not respect geographical boundaries. When countries work together, they can pool their resources, expertise, and knowledge to create more resilient health systems that can quickly respond to emerging threats. Your engagement in these cooperative efforts can lead to improved health policies and practices, benefiting not only your own nation but the entire European community.
Collaborative Health Initiatives
Collaborative health initiatives are vital for addressing health issues that affect multiple countries simultaneously. By participating in joint programmes, you can contribute to efforts aimed at combating infectious diseases, bolstering vaccination coverage, and developing strategies to handle public health emergencies. These initiatives often involve sharing best practices and lessons learned, allowing you and your neighbours to better equip yourselves against potential threats. The collective investment in these partnerships enhances the overall health security of the region and fosters a sense of solidarity among nations.
Information Sharing and Communication
Between nations, effective information sharing and communication are indispensable tools for enhancing health security. You must ensure that reliable and timely information flows seamlessly across borders, allowing for coordinated responses to health threats. Establishing robust channels for sharing data not only improves situational awareness but also enables you to respond more effectively to public health emergencies. This collaboration builds trust among countries, imperative for a unified approach to health security challenges.
Due to the interconnectedness of health concerns, the need for consistent communication among European nations cannot be understated. By sharing critical data on outbreaks, resource availability, and research findings, you will enhance your capacity to respond quickly and efficiently to potential threats. This reciprocal exchange strengthens the relationships between countries while fostering a climate of collaboration that can more effectively tackle future health emergencies, ultimately safeguarding the health of populations across Europe.
Addressing Socioeconomic Factors
All nations within Europe must take proactive measures to address the underlying socioeconomic factors that impact health security. By prioritising economic stability, equitable access to healthcare, and social welfare systems, governments can significantly improve the overall health of their populations. Here are some important steps that can be taken:
- Implement policies that promote economic equality.
- Enhance funding for healthcare services in underserved areas.
- Encourage community-based health initiatives.
- Support education programmes that raise awareness about health issues.
By focusing on these key areas, inequalities can be reduced, and the accessibility of healthcare improved, leading to more resilient communities. For more insight into this topic, visit Health Security means a Strong Europe. Knowing that your actions can help strengthen health systems across Europe brings an empowering sense of purpose.
Inequality and Accessibility Issues
About the disparities in healthcare access, it is important to recognise that health outcomes are often tied to socioeconomic status. Individuals from marginalised groups frequently experience barriers to accessing quality healthcare, which can lead to exacerbated health issues. Creating equitable healthcare frameworks requires understanding these inequalities and designing policies that address the unique challenges faced by disadvantaged communities.
Moreover, statistical data reveals that economic hardship significantly correlates with poorer health outcomes. By investing in comprehensive health services and equitable distribution of resources, your government can ensure that all citizens, regardless of their social standing, have the opportunity to achieve optimal health.
Community Engagement and Education
Beside addressing socioeconomic factors, fostering community engagement is vital for ensuring effective health security in Europe. By encouraging individuals to participate in local health initiatives, you can create a sense of ownership and responsibility towards personal and public health. Educational programmes can raise awareness about health topics and empower citizens to make informed decisions regarding their wellbeing.
Also, incorporating community feedback into health policies can lead to more effective strategies tailored to local needs. Promoting partnerships between government agencies, non-profit organisations, and community members fosters a comprehensive approach to health security, enabling everyone to play a role in enhancing public health outcomes.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
Keep in mind that the landscape of health security in Europe is continually evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities that must be navigated wisely. As you engage with the ongoing discussions surrounding Health sovereignty, you will recognise that fostering resilient health systems is imperative. The interplay between national interests and collective action can either hinder or enhance the efforts towards a unified health strategy, which is vital for addressing emergent health crises effectively. By focusing on proactive steps that integrate diverse perspectives, you can contribute to a robust framework that anticipates future health threats.
Emerging Health Threats
One of the pressing concerns you must contend with is the rise of emerging health threats, including infectious diseases, antimicrobial resistance, and the impact of climate change on health systems. These threats often transcend national borders, necessitating a collaborative approach among European nations to share information swiftly and develop joint strategies. Strengthening surveillance systems, improving data sharing, and ensuring quick response mechanisms are imperative to mitigate the effects of these health challenges.
Innovations in Health Security
Behind the scenes, various innovations are revolutionising health security frameworks across Europe. From advanced technology in disease monitoring to novel vaccine development, you will find that these advancements can significantly enhance your nation’s health resilience. Embracing digital health solutions, including telemedicine and electronic health records, can streamline healthcare delivery and improve access, particularly during crises. These innovations not only foster greater efficiency but also empower individuals to take charge of their health.
Considering the potential of these innovations, it becomes evident that embracing a culture of collaboration and adaptability is key to navigating future health challenges. By prioritising investment in research, development, and technology, you can help create a health ecosystem that is not only reactive but also proactive. This ensures that European nations are equipped to respond effectively to unforeseen health threats while capitalising on opportunities that arise in an increasingly interconnected world.
To wrap up
With this in mind, you should appreciate the significance of proactive steps in ensuring health security within European politics. By advocating for policies that prioritise public health, you can contribute to a more robust framework that addresses both immediate and long-term health challenges. Engaging with health authorities and policy-makers not only amplifies your voice but also fosters collaboration across nations, enabling the sharing of best practices and resources. Your involvement in these discussions can drive the agenda towards sustainable health solutions that benefit all citizens.
Additionally, you may want to consider the importance of ongoing education and community engagement in fostering a culture of health security. By promoting awareness and understanding of health issues within your community, you can empower others to take part in preventive measures. Active participation in local health initiatives and supporting research can also strengthen the collective response to health threats. Ultimately, your commitment to these proactive steps can significantly enhance the health resilience of Europe as a whole.
FAQ
Q: What are the key proactive steps that can be taken to ensure health security in European politics?
A: Key proactive steps include enhancing surveillance systems to monitor health threats, improving intergovernmental cooperation among EU member states, investing in health infrastructure, and ensuring that healthcare policies are prioritised in political agendas. Furthermore, public health awareness campaigns can empower citizens to take action towards their own health security.
Q: How can European nations collaborate on health security?
A: European nations can collaborate on health security by establishing joint health initiatives, sharing data on health risks, and coordinating responses to health emergencies. This can be achieved through platforms such as the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and collaborative research projects that tackle shared health challenges.
Q: What role does funding play in health security within European politics?
A: Funding plays a significant role in health security, as adequate financial resources are necessary for effective health programmes, research initiatives, and emergency preparedness efforts. Governments should allocate appropriate budgetary resources to ensure that public health systems are resilient and capable of responding to crises.
Q: How can public engagement influence health security policies in Europe?
A: Public engagement is vital for shaping health security policies because it encourages transparency and responsiveness from policymakers. Facilitating open dialogues between citizens and government officials allows for valuable feedback and ensures that health policies reflect the needs and concerns of the population.
Q: What impacts does climate change have on health security in Europe?
A: Climate change poses significant risks to health security by exacerbating health issues such as respiratory diseases, heat-related illnesses, and the spread of infectious diseases. European politics must incorporate climate considerations into public health strategies to mitigate these risks and adapt health systems accordingly to endure the effects of climate change.
Health & Society
How To Build Resilient Health Systems – Coordinated European Responses

Many individuals and communities rely on effective health systems, particularly during crises. To ensure maximum efficiency and better outcomes, you must focus on developing coordinated responses across Europe. This approach not only strengthens your local health infrastructure but also fosters collaboration among nations, enabling a more robust response to public health challenges. In this guide, you’ll learn the necessary steps to enhance resilience in your health system, paving the way for a healthier future.
Understanding Resilient Health Systems
To truly comprehend what constitutes a resilient health system, you must acknowledge its ability to respond effectively to various challenges while maintaining necessary health services. A resilient health system can withstand shocks, whether they stem from public health emergencies, such as pandemics, or other systemic pressures like economic downturns. The resilience of such systems is not merely in their robustness, but in their agility and adaptability to changing circumstances, allowing them to bounce back swiftly from disruptions while continuing to deliver high-quality care to all.
Key Characteristics of Resilience
Assuming you want to identify the key characteristics that define resilience in health systems, you will find that flexibility, adaptability, and resourcefulness are paramount. These characteristics enable health systems to adjust to evolving needs, manage unpredictable demands, and deploy resources efficiently in response to crises. Furthermore, an emphasis on collaboration within and between health services enhances the ability to share knowledge, skills, and resources, significantly strengthening overall health system resilience.
Importance of Coordination in Health Responses
While addressing health emergencies, you must understand that coordination plays a vital role in the effectiveness of responses. The integration of efforts across various health sectors ensures a unified approach that maximises the use of available resources and minimises redundancies. This coordinated effort not only fosters better communication among stakeholders—such as health officials, government entities, and non-governmental organisations—but also enhances your ability to implement interventions swiftly and at scale, ultimately saving lives and preserving health infrastructure during crises.
Another key consideration is that effective coordination facilitates the alignment of objectives and strategies across different organisations and regions, allowing for a more focused deployment of efforts. This integration can lead to improved health outcomes by ensuring that the right resources reach the right places at the right time. By establishing clear communication channels and protocols, you can greatly enhance the synergy between health services and stakeholders, creating a robust framework that fosters not just immediate responses, but long-term improvements in health system resilience.
Factors Influencing Resilient Health Systems
Now, the resilience of health systems is shaped by a myriad of factors that hold significant importance in fortifying their ability to withstand shocks and respond effectively. You must consider several key elements that play a vital role in shaping these systems:
- Governance
- Policy Frameworks
- Financial Sustainability
- Resource Allocation
- Collaboration
This multifaceted approach to understanding resilience allows for a comprehensive strategy in health system development.
Governance and Policy Frameworks
If you want your health system to be resilient, you need to ensure that robust governance and sound policy frameworks are in place. Effective governance involves not only strategic oversight but also the empowerment of local health authorities to make decisions that best serve their populations. The policies that underpin health systems must be flexible enough to adapt to emerging challenges, including pandemics and economic crises.
Additionally, transparent decision-making processes and stakeholder engagement are integral to building trust within the community. Your governance structures should promote accountability and encourage feedback from both health workers and the public, ensuring that policies remain relevant and effective in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
Financial Sustainability and Resource Allocation
Assuming financial sustainability is a foundational pillar for resilient health systems, it’s crucial that adequate resources are allocated to meet both current and future healthcare needs. You should scrutinise funding modalities and ensure that they are directed towards vital areas that enhance system strength, such as infrastructure, human resources, and technology. An effective resource allocation strategy can determine your health system’s capacity to respond to crises and maintain crucial services.
To succeed in financial sustainability, it is imperative that you prioritise investment in preventive care and community health initiatives. Underfunding these areas can result in significant long-term costs for your health system. Additionally, consider exploring diverse financing options, including public-private partnerships, which can bolster your system’s financial base. An effective allocation of resources not only promotes equity and access but also enhances the overall resilience of your health framework, allowing you to better navigate challenges as they arise.
How to Build Resilient Health Systems
Clearly, building resilient health systems is paramount for ensuring a responsive and robust healthcare environment capable of withstanding various challenges, including pandemics, natural disasters, and sudden shifts in population health needs. A resilient health system not only effectively manages immediate health crises but also lays the groundwork for long-term sustainability and adaptability, fostering an environment where health services can continue to operate under stress. This involves a multi-faceted approach that integrates resources, technology, and human capital, all while maintaining a clear focus on the health outcomes of the population.
In achieving an effective health system, the coordination of various elements such as policy-making, financing, and service delivery is vital. Thus, it becomes imperative to ensure that health systems are designed with flexibility in mind, enabling them to evolve according to the changing needs and expectations of the communities they serve. By promoting collaboration between public and private sectors and engaging a broad array of stakeholders, resilient health systems can be established that prioritise equitable access and quality care.
Engaging Stakeholders Effectively
You play a pivotal role in engaging stakeholders to create a robust health system. Effective stakeholder engagement means identifying key partners including healthcare professionals, policymakers, community organisations, and the public. It is vital to communicate clearly and frequently, establishing trust and fostering teamwork throughout the entire health landscape. Regular dialogue allows for the sharing of ideas and concerns, ultimately leading to shared ownership of health priorities and strategies. Involving stakeholders in decision-making processes ensures that the systems developed reflect the true needs and nuances of the communities they are intended to serve.
Moreover, cultivating strong relationships with your stakeholders enhances the sustainability of initiatives aimed at improving health systems. Engaging in active listening and collaborative problem-solving fosters a culture of inclusivity and respect. You can benefit from leveraging local knowledge and expertise, and in doing so, catalyse innovative solutions that are both creative and effective, ultimately leading to a better health system.
Implementing Evidence-Based Practices
Stakeholders are responsible for implementing evidence-based practices, which are vital for driving improvements in health systems. It is vital to integrate the best available research evidence into clinical decision-making and healthcare policies. By using data-driven strategies, you can ensure that interventions are not just implemented but are also evaluated for their effectiveness, allowing for ongoing improvements and refinements to service delivery. This provides a structure for moving away from anecdotal practices towards more scientifically validated approaches that can significantly enhance patient outcomes.
Effectively utilising evidence-based practices requires a strong commitment to continuous learning and adaptation. Health professionals and organisations should prioritise up-to-date training and education, encouraging them to seek out and apply new findings from research and clinical studies. Establishing a culture of inquiry within your health system enables quick adoption of successful practices while simultaneously identifying and mitigating potential risks, all of which contribute positively to the overall health landscape.
Tips for Coordinated Responses in Health Systems
Keep in mind the following strategies to enhance the coordination of your health system responses:
- Focus on establishing clear roles and responsibilities.
- Encourage ongoing training and capacity building.
- Promote inter-sectoral collaboration.
- Share data and insights regularly across stakeholders.
- Engage the community to foster trust and support.
This approach will not only improve your health system’s effectiveness but also build a foundation for sustained resilience.
Establishing Effective Communication Channels
If you want to facilitate a smooth and efficient health crisis response, establishing effective communication channels is imperative. Clear and concise communication ensures that all stakeholders are informed, reducing the chances of miscommunication and enhancing the overall operation of your health response. Regular updates, shared among all participants, can help in synchronising actions and keeping the focus on the common goals of your health systems.
In addition, adopting a multi-channel approach—utilising emails, instant messaging, and formal reports—can help cater to the varying preferences of stakeholders. Make sure to gather feedback to adjust your communication methods accordingly to fit evolving needs. This proactive approach will not only strengthen relationships but also prepare your health system for future challenges.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Collaboration
An effective way to improve collaboration within your health system is by leveraging technology. Utilising digital platforms and tools can significantly streamline communication, foster teamwork, and enhance information sharing among professionals. Tools such as collaborative project management software or data-sharing platforms facilitate transparency and enable real-time updates, ensuring everyone is working with the latest information.
Collaboration through technology allows your health system to effectively connect various stakeholders, streamline processes, and quickly adapt to changing situations. For example, virtual meetings and telehealth solutions allow for comprehensive discussions and consultations without geographical hindrances. The potential to share critical data across borders can improve your capacity to respond to health crises even faster. Additionally, security features in modern technologies should be prioritised to protect sensitive patient information, mitigating risks associated with data breaches. Always ensure that your technology choices enhance accessibility while maintaining robust security protocols in your health system.
Evaluating Resilience and Adaptability
Your ability to evaluate the resilience and adaptability of health systems is vital for ensuring that they can withstand and respond to crises. Resilience in healthcare implies a system’s capacity to absorb shocks, adapt to challenges, and drive recovery efforts effectively. To build a robust health system, it is important to focus on both qualitative and quantitative measures that underscore operational efficiency, stakeholder engagement, and the system’s capacity to learn from past experiences.
Your approach should incorporate feedback mechanisms that facilitate continuous evaluation and adjustment. Through simulations, scenario-based assessments, and stakeholder interviews, you can gain insights into how well the system has performed during stress events. This conscious back-and-forth process ultimately leads to a healthier and more prepared health system that safeguards public wellbeing.
Metrics for Assessment
With various metrics available, it is imperative to utilise a combination of both performance indicators and qualitative assessments to gauge resilience effectively. Key performance indicators such as patient outcomes, resource allocation efficiency, and healthcare service accessibility are important metrics to consider. Additionally, qualitative factors, including stakeholder satisfaction surveys and community engagement levels, provide a deeper understanding of the health system’s adaptability and trustworthiness.
With the right metrics in place, you can benchmark progress over time, identifying areas for enhancement and ensuring that health systems are not only responsive but also capable of evolving in the face of emerging challenges. This data-driven approach empowers you to instigate informed policy changes that can significantly improve health system resilience.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Some effective strategies for continuous improvement include fostering a culture of open communication, encouraging innovative practices, and implementing training programs focused on crisis management. By prioritising ongoing education and professional development, you strengthen the capabilities of healthcare professionals, ensuring they are equipped to tackle unforeseen challenges effectively.
The key to developing a more adaptable health system lies in integrating lessons learned into everyday practices. This might involve establishing dedicated task forces to analyse past incidents, soliciting feedback from frontline employees, or leveraging technology for data analytics. By focusing on continuous improvement, you ensure that your health system not only survives crises but also flourishes in its aftermath. This proactive stance is instrumental in building public confidence and promoting a healthier society overall.
Future Directions for Health System Resilience
Despite the challenges faced during recent health crises, there remains a significant opportunity to enhance the resilience of health systems across Europe. You may find it insightful to explore the Building a European Health Union initiative, which aims to coalesce efforts among member states, strengthening not only the capability to respond to future health emergencies but also ensuring a consistently high standard of care throughout the continent. Emphasising collaboration and unity among countries is imperative as health threats know no borders, requiring a unified approach to healthcare delivery. Understanding these future directions will equip you with the insights necessary to navigate evolving health landscapes.
Innovations in Health Care Delivery
Now, the integration of innovative technologies in health care delivery is swiftly transforming the way services are provided. From telemedicine to AI-driven diagnostics, these advancements enable you to access healthcare more efficiently during challenging times. Innovations like remote consultations can significantly reduce the burden on physical healthcare facilities while providing timely medical support, enhancing patient outcomes. As such technologies continue to develop, you will likely see a shift towards a more patient-centred healthcare model, empowering individuals to take charge of their own health.
Strengthening International Collaboration
An imperative component of building resilient health systems is the enhancement of international collaboration. This involves sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices among nations to tackle shared health challenges effectively. As you consider the importance of such partnerships, it becomes evident that collaborative efforts can lead to more rapid responses in times of crisis, and ensure that there is a collective approach in maintaining public health. Strengthening these ties is vital, especially as globalisation continues to influence health dynamics.
It is imperative to recognise that effective international collaboration not only supports immediate responses to health emergencies but also paves the way for long-term strategic planning. By pooling resources and expertise, countries can identify emerging public health threats, thus preventing potential future crises. This global solidarity is not just beneficial but necessary, as it strengthens your local health systems while ensuring a resilient response to health challenges faced worldwide. Ultimately, reinforcing international connections will allow you to contribute to a more stable and healthy future for everyone.
To wrap up
Taking this into account, you should recognise that building resilient health systems is not just a goal but a necessity in the face of evolving global health challenges. By fostering coordinated responses across Europe, you can ensure that resources are optimally shared, knowledge is effectively exchanged, and best practices are implemented to enhance your health sector’s robustness. It is vital that you actively contribute to these collaborative efforts, whether through local initiatives or wider networks, to create a more united and prepared healthcare system.
Your role in this process involves advocating for policies that support integration, investment in health infrastructure, and strengthening partnerships across borders. By prioritising these aspects, you can help cultivate a health system that adapts swiftly to changing circumstances, ultimately safeguarding the wellbeing of your community and beyond. Engaging with policymakers, healthcare providers, and fellow citizens will empower you to influence the direction of health system resilience, ensuring that your voice is part of the collective endeavour towards a healthier Europe.
FAQ
Q: What are resilient health systems?
A: Resilient health systems are those that can effectively respond to a wide range of challenges, including emergencies, pandemics, and changing health needs. They maintain crucial services during crises while being adaptable to recover from disruptions. Key components include strong leadership, efficient resource management, and integrated health services that ensure continuity and accessibility for all populations.
Q: How can European countries improve their coordinated response to health crises?
A: Improving coordinated responses in Europe requires enhanced communication and collaboration among countries. Establishing common protocols for data sharing, aligning public health guidelines, and creating joint training programmes for healthcare professionals are crucial. Additionally, fostering strong partnerships between governmental agencies and public health organisations can help streamline efforts to address health emergencies across borders.
Q: What role do technology and data play in building resilient health systems?
A: Technology and data are vital for building resilient health systems as they enable real-time monitoring of health trends and facilitate rapid responses to emerging threats. Advanced data analytics can help in predicting outbreaks and understanding public health needs. Moreover, telehealth services can improve access to care, especially during crises when physical access to healthcare facilities may be limited.
Q: How can community engagement contribute to health system resilience?
A: Community engagement is crucial for health system resilience as it fosters trust and encourages local populations to participate in health initiatives. Involving communities in decision-making processes enhances awareness about health issues and ensures that services are tailored to meet local needs. Strengthened community ties can also facilitate better compliance with health measures during crises, ultimately enhancing overall public health outcomes.
Q: What are the main challenges faced by European countries in achieving coordinated health responses?
A: European countries face several challenges in achieving coordinated health responses, including disparate healthcare policies, varying levels of funding, and differences in public health capacities. Cultural differences and language barriers can impede effective communication among nations. Additionally, the varying degrees of commitment to collaboration at political and organisational levels can hinder unified efforts to build resilient health systems across the continent.
Health & Society
Socioeconomic inequalities drive significant gaps in access to mental health care across the European Union

A study presented at the European Psychiatric Association Congress 2025 reveals deep socioeconomic inequalities in reported need for mental health care across the European Union. The research highlights how financial barriers disproportionately affect lower-income individuals, with significant disparities also linked to education level, whether the person lives in a city or in the countryside, and geographic location.
Led by Dr. João Vasco Santos, a public health physician, health economist, and professor at the University of Porto, the cross-sectional analysis used data from the 2019 European Health Interview Survey (EHIS), covering 26 EU member states. The survey among others asked participants whether they had gone without needed mental health care in the previous 12 months due to financial constraints.
Measuring Unmet Needs: A Financial Lens
The EHIS captures self-reported experiences, focusing specifically on financial reasons as a barrier including to accessing mental health services.
Across the EU, the proportion of self-reported unmet needs for mental health care varied widely — from as low as 1.1% in Romania to as high as 27.8% in Portugal, with a median of 3.6%.
Dr. Santos emphasized that while many European countries have moved toward mixed health systems — blending elements of Beveridge- and Bismarck-style models — financial protection remains inconsistent. Even in countries with universal coverage, out-of-pocket costs for medications, therapy, diagnostic testing, or medical devices can create substantial barriers.
“This is not just about whether care is public or private,” explained Dr. Santos. “Even in systems that are largely public, co-payments can be a burden. And sometimes, vulnerable groups—like migrants or asylum seekers—are excluded altogether.”
Cultural Perceptions Shape Reporting
One of the most striking findings was the stark contrast between Romania and Portugal. Dr. Santos cautioned against interpreting these figures at face value.
“It’s not just about the availability of services — it’s also about awareness and cultural perception,” he said. He noted that in Portugal, “we’re increasingly open about mental health and the mental health service.”
Portugal has been one of the countries that is spearheading the new perception of mental health care. “The UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities laid the foundation for the much-needed paradigm shift in mental health. From an exclusively medical approach to one based on the respect of the human rights of persons with mental health conditions and psychosocial disabilities,” Ms Marta Temido, Minister of Health of Portugal told during a United Nations consultation meeting in 2021.
Ms Marta Temido stressed that “In Portugal, we have been making significant efforts to align our laws, policies and practice with human rights.”
She specifically pointed out that “We have clearly made an option for community-based mental health services instead of institutionalization. We have been improving access to outreach care, through the launching of community teams for adults and for children and adolescents.”
In countries like Romania, stigma remains high, and is influenced by a long history of institutionalized care that fails to meet basic human standards. It should be obvious that if the psychiatric system hasn’t evolved much beyond large psychiatric institutions with reported human rights violations, one might think twice before reporting need of help.
Dr. Santos noted that in countries where mental illness is stigmatized or misunderstood, individuals may avoid reporting symptoms altogether. In some cases, people may not perceive a need for care because of limited exposure to mental health education or fear of discrimination.
Education and Inequality
The study also revealed a strong correlation between educational attainment and unmet needs. In 15 out of 26 countries analyzed, individuals with only primary education were significantly more likely to report going without mental health care than those with tertiary education.
“In Bulgaria, Greece, Romania, and Slovakia, this disparity is especially pronounced,” Dr. Santos noted. The pictures across the European countries however is quite complex, as exemplified with France where the opposite is the case. In France people with tertiary education showed a higher unmet need of mental health care. This indicate that further studies may be needed which could look at adjusting for income and other factors. The study conducted only considered the educational related inequalities.
Pandemic Impact and Future Trends
Although the study drew on pre-pandemic data (from 2019), Dr. Santos warned that the pandemic likely exacerbated existing inequalities.
“We know that mental health deteriorated during the pandemic — there was increased violence, isolation, and trauma,” he said. “At the same time, access to care was disrupted. I suspect the next wave of data will show a rise in unmet needs, particularly among lower-income and marginalized groups.”
However, he stressed that longitudinal comparisons must be made carefully, noting that changes in survey design over time can affect results.

“The goal must be to leave no one behind,” Dr. João Vasco Santos
Policy Recommendations addressing socioeconomic inequalities
To address these systemic challenges, Dr. Santos outlined a series of priorities that require coordinated action at both national and regional levels.
First, he emphasized the importance of expanding universal coverage to ensure that all individuals — including migrants and asylum seekers — have access to essential mental health services without facing financial hardship. He called for reforms that would exempt low-income and chronically ill populations from co-payments, even in systems where care is otherwise publicly funded.
Second, he advocated for a shift toward community-based care models, which improve accessibility, reduce stigma, and foster integrated, person-centered treatment approaches.
Third, Dr. Santos underscored the need for national and regional mental health strategies that incorporate public education campaigns aimed at improving health literacy.
“The goal must be to leave no one behind,” he concluded. “Health is an investment — not just in individuals, but in the resilience and equity of society as a whole.”
Health & Society
More than 30 years of difference in life expectancy highlights health inequalities

The study of the World Health Organization (WHO) reveals that they can be responsible for a Spectacular reduction in life expectancy in rich and poor countries.
For example, People living in the country with the highest life expectancy will live on average 33 years more than those born in the country with the lowest life expectancy.
An unequal world
“Our world is uneven. Where we were born, grow, live, work and age considerably influence our health and well-being, “said Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus.
Health inequalities are closely linked to the degrees of social disadvantage and the levels of discrimination.
“” Health follows a social gradient by which the area in which people live more disadvantaged, the more their income is lowWho said.
Inequalities are particularly exacerbated in populations faced with discrimination and marginalization, such as indigenous peoples, who have lower expectations of life than their non -Aboriginal counterparts.
This is the case in high -income and low -income countries.
Key targets at risk
The study is the first to be published since 2008, when the WHO Social Health Determinants of Health Declines published its final reporting objectives for 2040 to reduce gaps between and within countries in life expectancy, childhood and maternal mortality.
It shows that these objectives are likely to be missed, and despite a rarity of data, there is sufficient evidence to show that health inequalities have often expanded.
For example, children born in poor countries are 13 times more likely to die before their fifth anniversary than in richer countries.
In addition, modeling shows that the life of nearly two million children per year could be saved by filling the gap and improving equity between the poorest and richest populations of the population in low and average income countries.
In addition, although maternal mortality has decreased by 40% between the 2000s and 2023, the majority of deaths, 94%, still occur in low and lower income countries.
Appeal to action
Who calls for collective action to deal with economic inequalities and invest in social infrastructure and universal public services.
The agency also recommends other stages, in particular on the survival of structural discrimination and the determinants and impacts of conflicts, emergencies and forced migration.
Originally published at Almouwatin.com
-

 EU & the World6 days ago
EU & the World6 days agoWho Is Valeria Marquez? About the Influencer Who Was Shot During Livestream
-

 EU & the World4 days ago
EU & the World4 days agoChris Brown Tour 2025: Updates on Concert Dates, Cities, Ticket Prices & More
-
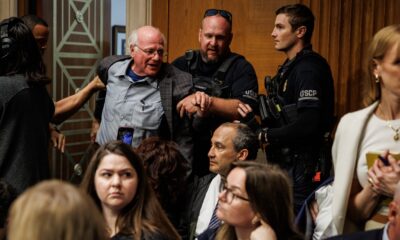
 EU & the World5 days ago
EU & the World5 days agoWho Is Ben Cohen? About the Ben & Jerry’s Co-Founder Who Was Arrested During Senate Hearing
-

 EU & the World3 days ago
EU & the World3 days agoJosh Freese: 5 Things to Know About the Former Foo Fighters Drummer
-

 EU & the World5 days ago
EU & the World5 days agoChris Brown’s Net Worth: How Much Money He Makes Now
-
Travel7 days ago
Crete earthquake: Is it safe to travel to the Greek island following tsunami warning?
-

 Entertainment4 days ago
Entertainment4 days agoEurovision 2025: Music, Politics, and the Final 26 Set Amid Controversy and Spectacle
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoFerrari, opposing views after first day at Imola for Charles Leclerc and Lewis Hamilton